- Home
- Why Truffles?
- Blog
- You Can't Run from Vein Disease
- VenaSeal
- Summer is Almost Over
- IDK about Vein Disease
- Vein Treatment Fayetteville
- Sonography to RN Degree Program
- Vein Testing Differences
- Advantage of Vein Treatment Before Knee Surgery
- Poor Medical Advice
- Green Tomatoes for Varicose Veins
- VenaSeal Treatment Atlanta
- Fake News
- Iliac Vein Compression
- Vein Treatment
- DVT
- Pelvic Health
- Sclerotherapy
- leg swelling
- The Vein Specialists
- Vein Treatments
- What is Vein Disease
- Vein Conditions
- Vascular Testing
- Look and Feel Your Best!
- Reviews
- Media
- Contact Us
- Schedule and Appointment
- Free Vein Screening
- Give Us Feedback
- Referral Resources
- Make a Payment
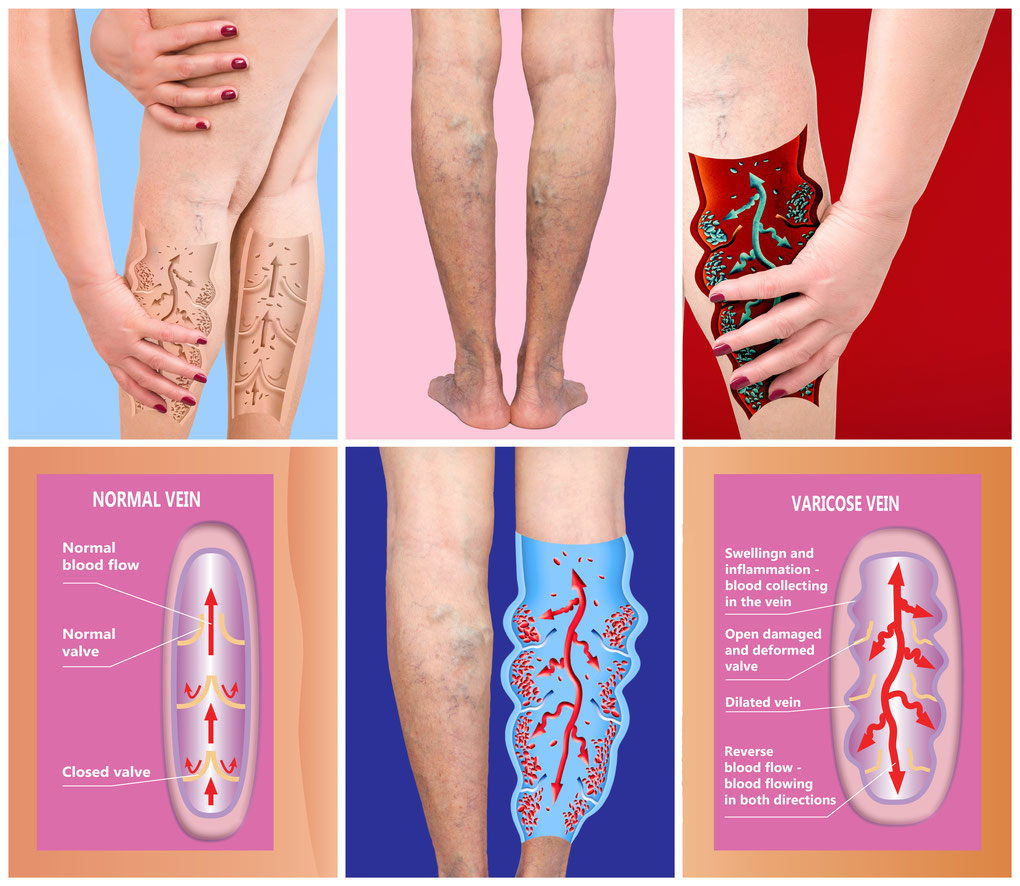
Deep Vein thrombosis (DVT) - Truffles Vein Specialists
If the venous blood moves too slowly through your veins, it can cause blood cells to clump together; this is called a clot. When a blood clot forms in a vein deep inside your body, it causes what doctors call “deep vein thrombosis” (DVT). This is most likely to happen in your lower leg; however, it can occur in your thigh or pelvis. Blood clots can occur in other parts of your body, too. DVT can lead to significant health problems. In some cases, it can be fatal. That’s why you must immediately seek medical attention if you think you have one.
What Are the Signs of Deep Vein Thrombus (DVT)?
Not everyone with DVT shows symptoms. But you might notice any of the following:
- Leg or arm swelling that comes on without warning
- Pain or soreness when you stand or walk
- Warmth in the area that hurts
- Enlarged or dilated veins
- Cramping sensation in the calf that just won't go away
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
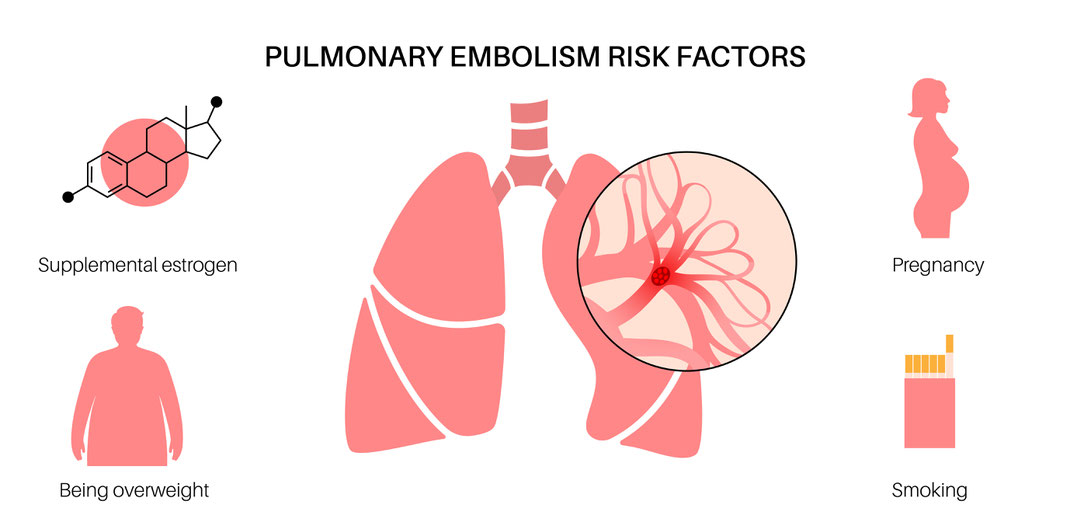
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is when a blood clot breaks free and moves through your veins. It travels to your lung and gets stuck in a blood vessel that provides oxygen to the lungs. Doctors call this a pulmonary embolism, or PE. It can be fatal or cause significant long-term disability. PEs can vary in size, and most fatal PEs are from large blood clots that travel from the legs or pelvis. How big is a blood clot? It surprises most people that many healthcare physicians do not understand blood clots or DVTs and how they affect their patients.
Some people don't know they have DVT until a PE happens.
Signs of PE include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain that's worse when you take a deep breath
- Coughing up blood
- Increased heart rate
What Causes DVT?
Many things can increase your likelihood of getting DVT. Here are the most common:
- Change in Blood Chemistry: Hormones play a massive part in the risk assessment for DVT. Birth control, estrogen and testosterone injections, supplements, or pills increase the risk for DVT.
- Aging. Deep vein thrombus (DVT) can happen at any age; however, your risk is greater after age 35.
- Sitting for long periods. When you sit or lie down for extended lengths of time, the venous blood flow in your legs pool or become stagnant. Muscle contraction is the heart of the venous system; sitting makes it hard for blood in the veins to move around as it should. Extended bed rest, long car rides, or flights over four hours put you at risk for developing thrombus or DVT.
- Pregnancy. Carrying a fetus puts more pressure on the veins in your pelvis and legs. Statistically, 22-32% of people have iliac vein compression. Iliac vein compression is when the primary vein from the leg into the pelvis is compressed by another anatomical structure, commonly the artery. In pregnancy, the fetus can intrinsically cause compression increasing the possibility of developing DVT. Add in trauma and a change in blood chemistry through sedation, and the risk increases. In some women, a DVT can happen up to 6 weeks after they give birth.
- Trauma: An injury to the leg or other body parts increases inflammation and limits people's mobility. Inflammation and mobility combine to increase the risk of developing DVT.
- Obesity. Obese patients defined as a body mass index (BMI) over 30 have a higher risk of developing DVT.
- Cancer: It is estimated that nearly half of diagnosed asymptomatic DVT is due to an underlying malignancy.
Imaging of Calf Veins
Did you know that the American College of Radiology doesn't require imaging below the knee!
Radiology Department often misses up to 50% of deep vein thrombosis due to poor imaging protocols.
An 8-year study showed that 98% of DVT found above the knee had calf involvement and that 54% of the patients who had confirmed DVT would have been called normal if the calf was not imaged.
Dedicated Vascular Lab
If you are having a vascular ultrasound performed, it should be by a Registered Vascular Technologist or Sonographer. RVT or RVS. Even then, as a patient, it is your right to know how much experience they have. Ask questions; it is your right!
Advanced Reporting
We use Core Study Cast cloud based PACS. This enables us to share your test and the images anywhere in the world immediately.